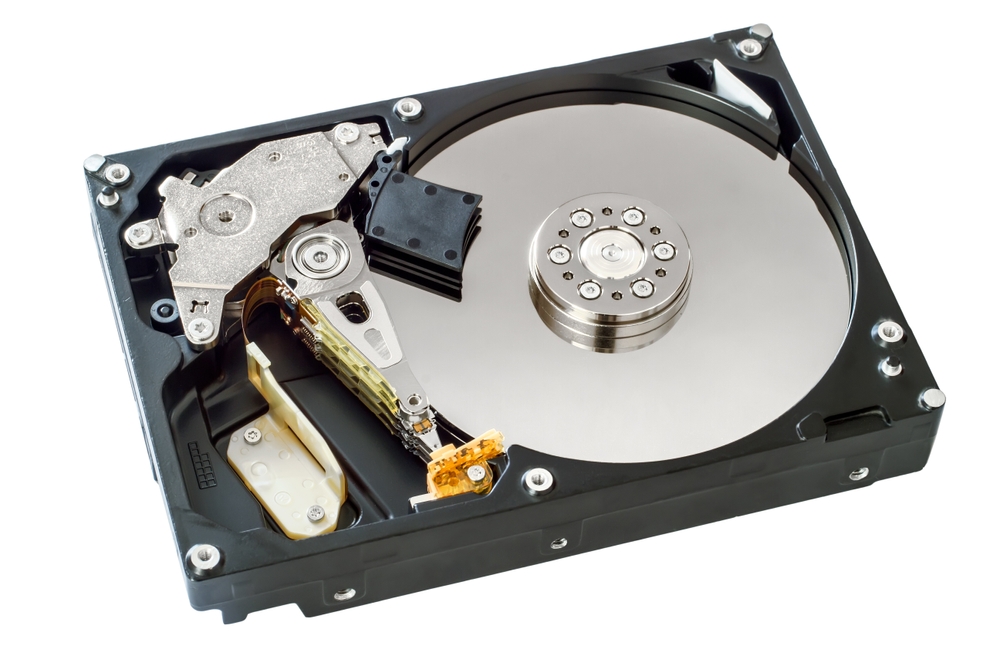
Introduction to Server Hard Drives
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, the backbone of any efficient IT infrastructure is reliable storage. Server hard drives are critical components in ensuring optimal performance, data accessibility, and scalability. Unlike consumer-grade storage devices, server hard drives are engineered to handle 24/7 operations, manage heavy workloads, and support enterprise-level IT hardware demands.
From ensuring the smooth operation of applications to safeguarding mission-critical data, server hard drives play a pivotal role in the success of computer hardware ecosystems.
The Importance of Server Hard Drives in IT Hardware
Every IT infrastructure, regardless of its size, requires robust storage solutions. The server hard drive serves as the central repository for an organization’s data, including databases, virtual machines, and backup files. These drives are specifically designed for server environments, where uptime, speed, and reliability are paramount.
Unlike regular storage devices, server hard drives are built to withstand continuous operations in demanding conditions. They are essential in reducing latency, preventing downtime, and ensuring seamless data transfer across networks.
Types of Server Hard Drives
Understanding the types of server hard drives is crucial when selecting the right solution for your needs. Each type comes with unique features and is suited for specific use cases.
1. HDDs (Hard Disk Drives)
Traditional hard disk drives are widely used in server environments due to their affordability and capacity. Key features include:
- High storage capacities (up to 20TB or more)
- Cost-effective for bulk storage
- Suitable for archive or backup purposes
However, HDDs have slower read/write speeds compared to SSDs, making them less ideal for performance-intensive tasks.
2. SSDs (Solid-State Drives)
Solid-state drives have become the standard for high-performance server setups. Their advantages include:
- Faster data access speeds
- Greater reliability (no moving parts)
- Lower power consumption
- Enhanced durability
SSDs are ideal for applications requiring high-speed data processing, such as database operations or running virtual machines.
3. NVMe SSDs (Non-Volatile Memory Express)
For cutting-edge performance, NVMe SSDs are the preferred choice. They leverage PCIe interfaces for:
- Ultra-fast data transfer rates
- Lower latency
- Improved IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second)
NVMe drives are highly recommended for high-performance workloads, such as AI, big data analytics, and real-time applications.
4. Hybrid Drives (SSHDs)
Combining the affordability of HDDs with the speed of SSDs, hybrid drives offer a balanced solution. They use a small amount of solid-state storage to cache frequently accessed data, improving overall performance without the high cost of SSDs.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Server Hard Drive
Selecting the right server hard drive involves evaluating several critical factors:
1. Capacity
Storage capacity is one of the primary considerations. Assess your organization’s current and future storage needs. For archival purposes, HDDs with large capacities are ideal, whereas SSDs are better for environments that demand high-speed performance.
2. Performance
Performance metrics such as data transfer speed, latency, and IOPS are crucial for workloads like database queries and virtual environments. SSDs and NVMe drives offer significantly higher performance compared to traditional HDDs.
3. Reliability
In server environments, downtime is unacceptable. Look for drives with high Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and features like error correction technology to ensure long-term reliability.
4. Form Factor
Server hard drives typically come in two form factors:
- 3.5-inch drives: Common for HDDs and used in bulk storage.
- 2.5-inch drives: Common for SSDs and NVMe drives, allowing for higher density in server racks.
5. Interface
The drive’s interface determines its compatibility and speed. Common interfaces include:
- SATA (Serial ATA): Suitable for HDDs and SSDs; cost-effective but slower.
- SAS (Serial Attached SCSI): Offers better speed and reliability than SATA; common in enterprise environments.
- PCIe: Used by NVMe drives for superior performance.
6. Cost
Budget constraints often dictate storage decisions. HDDs are more cost-effective for large-scale storage, while SSDs, though pricier, deliver unmatched performance. Consider hybrid solutions to balance cost and efficiency.
RAID Configurations for Server Hard Drives
Most servers employ RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations to enhance storage performance and reliability. Popular RAID types include:
- RAID 0: Focuses on performance by stripping data across multiple drives but lacks redundancy.
- RAID 1: Mirrors data across two drives for redundancy but offers no performance boost.
- RAID 5/6: Balances performance and redundancy, with the ability to recover from one (RAID 5) or two (RAID 6) drive failures.
- RAID 10: Combines striping and mirroring for maximum performance and redundancy but requires more drives.
Choosing the right RAID configuration depends on your server’s workload and the criticality of your data.
Benefits of Upgrading Server Hard Drives
Upgrading your server hard drives can provide a host of benefits, including:
-
Improved Performance Switching from HDDs to SSDs or NVMe drives can drastically reduce data access times, improving application performance and user experience.
-
Enhanced Scalability Modern server hard drives support higher capacities and faster data transfer rates, enabling IT teams to scale as organizational needs grow.
-
Reduced Downtime Newer drives often include advanced error correction and self-monitoring technologies, minimizing the risk of IT hardware failure.
-
Lower Energy Costs SSDs and NVMe drives consume less power than traditional HDDs, reducing overall energy costs in large-scale server environments.
Server Hard Drive Maintenance and Best Practices
Proper maintenance of server hard drives ensures their longevity and optimal performance. Here are some best practices:
1. Regular Monitoring
Use monitoring tools to check the health of your drives. SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) can help predict drive failures before they occur.
2. Routine Backups
Always maintain up-to-date backups of critical data. Even with reliable drives, unforeseen issues like power surges or malware attacks can lead to data loss.
3. Optimize Cooling
Overheating can shorten a drive’s lifespan. Ensure adequate cooling in server rooms and monitor temperature levels.
4. Firmware Updates
Keep your drives’ firmware updated to benefit from the latest performance optimizations and security patches.
Common Myths About Server Hard Drives
Myth 1: Consumer Drives Are Enough for Servers
While consumer-grade drives may seem cost-effective, they are not designed for the rigorous demands of server environments. Always invest in drives specifically built for server use.
Myth 2: Higher Capacity Means Better Performance
Capacity does not equate to performance. Always evaluate factors like data transfer speeds and IOPS alongside capacity.
Myth 3: All SSDs Are the Same
Not all SSDs offer the same performance or durability. Enterprise-grade SSDs are optimized for server workloads and offer better endurance than consumer SSDs.
Emerging Trends in Server Storage
The server storage landscape continues to evolve. Key trends shaping the future include:
-
AI-optimized drive manufacturers are developing server hard drives tailored for AI workloads, offering faster data processing and reduced latency.
-
Hybrid Cloud Solutions Organizations are increasingly adopting hybrid solutions that combine on-premise server drives with cloud storage for greater flexibility.
-
Energy-Efficient Drives With a growing emphasis on sustainability, energy-efficient server drives are becoming a priority for environmentally conscious organizations.
Conclusion: Maximizing the Potential of Server Hard Drives
Server hard drives are indispensable to modern IT infrastructures, providing the foundation for data storage, processing, and accessibility. By carefully evaluating factors like performance, reliability, and capacity, organizations can select the ideal storage solution for their needs.
Whether it’s an HDD for archival purposes, an NVMe SSD for high-speed applications, or a hybrid approach to balance cost and performance, the right choice can elevate your server’s capabilities. With proper maintenance and a forward-thinking approach, server hard drives will continue to drive innovation and efficiency in computer hardware systems.
Investing in the right server hard drive isn’t just about storage—it’s about empowering your IT infrastructure for success.